Hipot test is short for “High Potential Test,” also known as the “Dielectric Strength Test.” It is used to measure the potential of an electronic device for higher than usual operating voltage. Hipot testers emit high voltage under test (DUT).
For the safe use of an electronic device, it is important to ensure that it can withstand a higher voltage than usual. Therefore, a hipot test is significant for safety and checking the reliability of the electrical insulation of an electronic device.

When you perform the hipot test, the device’s insulation prevents the extra current voltage from flowing to the device. Which can be harmful to it.
But If the insulation is not good enough, it breaks down, and a high voltage current starts to flow into the device. However, this leads to hazardous conditions.
Therefore, make sure to conduct hipot tests in safe environmental conditions.
Hipot Testing – Types and Production Line Hipot Test
As a type hipot test, this test determines the qualities and defects of a device during its design. It helps to identify any problem with the conductors and insulation. On the other hand, a production-line hipot test checks any error with the operation of a device and its safety.
So a hipot test covers all the testing necessary to detect any malfunctioning in a product. Also, its protection devices such as scrapes, pinholes, or moisture in insulations.
It ensures that it didn’t result from any defects in design or during construction. If it did, let the manufacturer or operator make necessary modifications.
Continuity Test and Hipot Test – Difference
A continuity test checks the proper operation, but it differs from the hipot test. A hipot test ensures that an unusual current will not flow to the device, while a continuity test ensures that the current will flow between the conductor and the device.
How Helpful is Hipot Testing?
When electrical devices expose to spikes or power surges, they should be able to hold out against heavy voltages. Therefore, proper insulation of these devices is done. The insulators don’t let the excess voltage flow to the device that it cannot withstand.
But sometimes, the insulation is weaker than the need of the device and fails to protect the device. The Hipot Testing process checks the insulation’s reliability and whether they meet the safety standards or not.
During the test, devices get high voltage for a while. This test is conducted for detecting defects in cables, transmitters, insulation devices, etc.
How Is a Hipot Test Conducted?
Only professionals with proper knowledge about the hipot testers and the device under test (DUT) conduct the Hipot Test.
Before starting, always wear insulating gloves for safety and don’t try to touch the cables during the test. Also, putting barriers around the test circuit doesn’t allow anyone to come near the testing area.
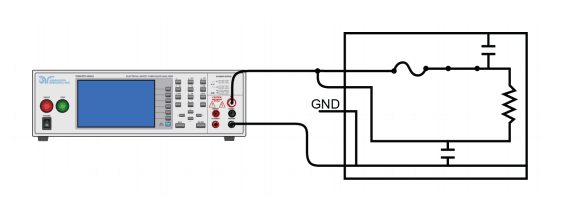
If you are testing a cable or circuit, ensure that there is no connection to any other cable for correct results. Now connect the wires of the hipot tester to the relative conductors. First, connect the ground wire to the ground conductor of the building and then connect the high voltage wire to the DUT.
Once you connect everything, switch on the AC hipot tester and set the required current and voltage meter. Usually, the current meter is set to 10mA, and the common hipot test voltage is 1500 volts. Or the test voltage is set about two times more + 1000 volts than the actual voltage of the device.
Now, record the reading, reset the voltage meter back to zero and the current meter to 10mA if you changed it during the observation as per the need. Now, turn off the hipot tester. Use a grounding stick instead of hands for removing the ground wire.
The test procedure is usually the same for both AC and DC hipot testers. However, the test voltage for a DC hipot test is 1.414 times higher than AC voltage. Therefore, a device being tested at 1500 volts by an AC hipot tester should be tested at 2121 volts by a DC tester.
Voltage AC or DC Hipot Testing
To decide the type of hipot test, check whether the device you are about to test is running on AC voltage or DC voltage, and then conduct the test accordingly. AC and DC tests both have some pros and cons.
For an AC hipot test, there is no need to ramp voltage for the changing polarity as it ramps up by itself. While for a DC hipot test, the voltage requires ramping, which means there is a need for a slight pause after each increase in voltage.
Also, an AC voltage test checks both polarities but the dc voltage test checks only one polarity. You don’t need to discharge your device after conducting an AC test. Besides, an AC test can measure real and reactive current both.

The safety agencies more widely accept AC Tests, but sometimes they conduct a DC test for its advantages. To conduct a DC voltage hipot test at a very low current level is safe for the operator.
A DC test measures the leakage current more correctly than an AC test. Moreover, a DC hipot test is more reliable for devices with higher capacitance.
Conclusion
Hipot testers are great for testing insulations and the safety of devices. However, these tests should only be performed by professionals.
The type testing and production-line hipot testing both help in the quality manufacturing and operating of devices and determine their safe use.